The National Pension System (NPS) is a voluntary retirement savings program designed to enable subscribers to make defined contributions towards planned savings, ultimately ensuring a secure future in the form of a pension. It represents an effort to provide a sustainable solution to the challenge of ensuring sufficient retirement income for every citizen of India. In this article, we are going to talk about the NPS scheme in detail. Stay tuned to understand about the scheme in detail.
Upon reaching the normal exit age from the NPS, subscribers have the option to utilize their accumulated pension savings within the scheme. They can choose to purchase a life annuity from a life insurance company that is empaneled by the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA). Alternatively, they may opt to withdraw a portion of their accumulated pension savings as a lump sum payment.
What is the National Pension System (NPS)?
The National Pension Scheme (NPS) is a government-backed social security program aimed at providing retirement benefits to individuals. This program is available to employees from various sectors, including public, private, and even the unorganized sectors, excluding those in the armed forces.NPS encourages people to contribute to a pension account regularly throughout their working years. Upon retirement, subscribers have the option to withdraw a portion of their accumulated savings as a lump sum, while the remaining amount is received as a monthly pension.
Initially, NPS was limited to Central Government employees, particularly those who joined after January 1, 2004. However, the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA) has expanded its scope to include all Indian citizens on a voluntary basis.
NPS offers significant advantages for individuals in the private sector who seek a dependable pension plan for their retirement. One of its key features is portability, which means that individuals can carry their NPS account across different jobs and locations.
The PFRDA serves as the central agency responsible for the implementation and oversight of the NPS.
| National Pension Scheme (NPS) 2023 Key Highlights | |
| National Pension Scheme Launch Date | January 1, 2004, |
| National Pension Scheme Official Website | Click Here |
| National Pension Scheme Objective | To help individuals make regular contributions for planned savings, ensuring a secure future through a pension. |
| National Pension Scheme Ministry | Ministry of Finance |
| National Pension Scheme (NPS) Interest Rate | 9% to 12% |
| National Pension Scheme Employee Contribution | 14% for Government Employees10% for Private and self-employed individuals |
| National Pension Scheme Tax Deduction Limit | Rs 1.5 Lakh Under 80CCE |
| National Pension Scheme Nature | Mandatory for Government EmployeesVolunstry for others |
| National Pension Scheme (NPS) TollFree Number for Registered Subscribers (with PRAN) | Offline/Online |
| National Pension Scheme Toll Free Number for Registered Subscribers (with PRAN) | 1800 222 080 |
| National Pension Scheme Helpline Number | 1800 110 708 |
National Pension System Benefits
i) Cost Effective:
NPS is recognized as one of the most cost-effective pension schemes globally. It boasts the lowest administrative charges and fund management fees.
ii) UserFriendly:
Opening an NPS account is a straightforward process. All an applicant needs to do is open an account with one of the Points of Presence (POPs) available at various Head Post Offices across India and obtain a Permanent Retirement Account Number (PRAN).
iii) Customizable:
Applicants have the flexibility to choose their preferred investment options and Pension Fund or opt for the Auto Choice feature to maximize returns.
iv) Portability:
NPS accounts are highly portable, allowing account holders to manage their accounts from anywhere in the country. Contributions can be made through any POPSP (Point of Presence Service Provider), regardless of the branch with which the applicant initially registered.
This portability remains intact even if the individual relocates to a different city or changes jobs. Additionally, contributions can also be made through eNPS. If a subscriber switches employment, the account can be transferred to another sector, such as the Government Sector or Corporate Model, as applicable.
READ ABOUT
National Pension System NPS Eligibility Criteria
To be eligible to join the National Pension Scheme (NPS), individuals must meet the following criteria:
1. Indian Citizenship: You can be either a resident or a non-resident Indian (NRI) to participate in NPS.
2. Age Range: Your age should fall within the range of 18 to 70 years to be eligible for NPS enrollment.
3. KYC Compliance: You must adhere to the Know Your Customer (KYC) norms specified in the NPS application form. This involves providing necessary identification and address verification documents.
4. Legal Competency: You should have the legal capacity to enter into a contract, as per the Indian Contract Act.
However, it’s important to note that Overseas Citizens of India (OCI), Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs), and Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs) are not eligible to subscribe to the NPS.
Furthermore, NPS is an individual pension account, which means it cannot be opened on behalf of a third person. Each individual must have their own NPS account if they meet the eligibility criteria.
Tax Benefits for Employees
Employee’s Own Contribution:
Employees who are actively contributing to NPS can avail of tax benefits on their personal contributions. These benefits are as follows:
- Eligible for a tax deduction of up to 10% of Salary (comprising Basic and DA) under Section 80 CCD(1).
- This deduction falls within the overall limit of Rs. 1.50 lakhs specified under Section 80 CCE.
Employer’s Contribution:
Additionally, employees can also receive tax benefits on their employer’s contributions, which are as follows:
- The employee can claim a tax deduction for contributions made by the employer, up to 10% of Salary (Basic + DA), under Section 80 CCD(2).
- Importantly, this deduction is in addition to the limit of Rs. 1.50 lakhs provided under Section 80 CCE.
Tax Benefits for Self-Employed Individuals:
For self-employed individuals, there are tax deductions available as follows:
1. A tax deduction of up to 10% of their gross income can be claimed under Section 80 CCD(1).
2. This deduction is within the overall limit of Rs. 1.50 lakhs set by Section 80 CCE for various tax-saving investments.
Furthermore, subscribers have the option to claim an additional deduction in their NPS account under Section 80 CCD(1B). This additional deduction is available for contributions beyond the regular limit and is subject to a maximum investment of Rs. 50,000.
Types of Accounts Under NPS
Tier I Account
The TierI Account is primarily a retirement savings account where the applicant contributes savings for their retirement. It is a restricted withdrawal account, meaning that there are limitations on when and how much can be withdrawn. Contributions made to this account are eligible for tax benefits in accordance with the prevailing Income Tax rules.
Tier II Account
The TierII Account, on the other hand, is a voluntary savings facility. Subscribers have the freedom to withdraw their savings from this account as and when they wish. Unlike the TierI Account, the TierII Account is not intended for retirement savings, and as a result, contributions to this account do not qualify for tax benefits.
| NPS Particulars | Tier I Account | Tier II Account |
| Status | Default | Voluntary |
| Withdrawals | As per the rules/regulations | Permitted |
| Tax exemption | Up to Rs 2 lakh p.a.(Under 80C and 80CCD) | 1.5 lakh for government employees Other employees- None |
NPS Contributions:
Subscribers have the flexibility to contribute funds to their NPS account through various means, including cash, local cheques, demand drafts, or Electronic Clearing System (ECS) at their chosen Point of Presence Service Provider (POPSP). However, it’s important to note that for cash transactions exceeding Rs. 50,000, the subscriber is required to submit a copy of their PAN card as per AntiMoney Laundering (AML) regulations. Additionally, outstation cheques will not be accepted.
Minimum Contributions (For TierI Account):
The minimum contribution required at the time of account opening and for all subsequent transactions is Rs. 500.
A minimum contribution of Rs. 1,000 per year is required, excluding charges and taxes.
Subscribers are expected to make at least one contribution per year.
Charges and Penalties for Noncompliance with Minimum Contributions:
If a subscriber contributes less than Rs. 1,000 in a year, their account will be frozen, and certain facilities provided by the Central Recordkeeping Agency (CRA), such as online account viewing, will be restricted.
To reactivate the account, the subscriber must make a minimum contribution of Rs. 500.
A frozen account will be closed when its value reaches zero.
Minimum Contributions (For Tier II Account):
- The minimum contribution required at the time of account opening is Rs. 1,000, and for all subsequent transactions, a minimum amount per contribution of Rs. 250 is required.
- There is no minimum contribution requirement for the financial year, and there is no upper limit on the maximum contribution.
| NPS Particulars | Tier I Account | Tier II Account |
| Minimum contribution for opening an account | Rs.500 | Rs.1,000 |
| Minimum NPS contribution | Rs 500 per month or Rs 1,000 p.a. | Rs 250 |
| Maximum NPS contribution | No limit | No limit |
Withdrawal Options in the National Pension System:
1. Upon Reaching Age 60:
- When a subscriber turns 60, they have several choices.
- They must use at least 40% of their accumulated pension savings to purchase an annuity, which provides a monthly pension.
- The remaining amount can be taken as a lump sum payment.
- If the total savings are less than Rs. 5 Lacs, the subscriber can choose to take the entire amount as a lump sum.
- Alternatively, they can defer the lump sum withdrawal until age 75 and continue contributing to the NPS until then.
- This choice must be made at least 15 days before turning 60.
2. Before Age 60 (After 10 Years in NPS):
- A subscriber can exit the NPS before turning 60, but only if they have completed at least 10 years in the system.
- At least 80% of their savings must be used to purchase an annuity for a monthly pension.
- The remaining balance can be taken as a lump sum.
- If the total savings are less than Rs. 2.5 Lacs, the subscriber can opt for a 100% lump sum withdrawal.
3. In the event of the Subscriber’s Death:
- If the subscriber passes away, the nominee (chosen by the subscriber) has options.
- The nominee can receive 100% of the NPS pension savings as a lump sum.
- Alternatively, if the nominee wishes to continue with the NPS, they must go through the Know Your Customer (KYC) process and subscribe to NPS individually.
In the National Pension System, the Central Recordkeeping Agency (CRA) is responsible for processing and settling all withdrawal claims. They have a specialized NPS claim processing cell (NPSCPC) for this purpose. The CRA ensures that withdrawal claims are processed according to the guidelines provided by the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA). Currently, the NPSCPC is fully operational.
This system ensures that subscribers have flexible options for accessing their pension savings, whether it’s upon retirement, before turning 60, or in the event of their demise. It’s essential to understand these withdrawal options and make informed decisions regarding your NPS savings.
National Pension System (NPS) Interest Rate
The interest rate in the National Pension Scheme (NPS) is not fixed and guaranteed in advance. Instead, it is dependent on the performance of the assets in which you choose to invest. NPS is essentially a market-linked investment product, which means that the returns you receive upon retirement cannot be predetermined.
When you participate in NPS, you have the opportunity to invest in a combination of asset classes, including equity, government debt, corporate debt, and alternative assets. After deciding on your preferred asset mix and selecting a fund manager, your contributions are invested in specific schemes that focus on these four asset classes.
Additionally, NPS offers the flexibility of having two types of accounts: Tier I and Tier II accounts. These accounts may have different returns based on the investment choices made within them.
| Tenure | Can invest till the age of 65 years |
| Interest rate | 9% to 12% p.a. |
| Investment Amount | Starting at Rs.250 |
| Maturity Amount | Depends on the investment amount |
It’s important to note that as of December 31, 2022, specific returns for NPS cannot be provided because they are subject to market performance and the asset allocation decisions made by the individual. The returns you ultimately receive will depend on the performance of your chosen investments over time.
In summary, NPS offers market-linked returns, and the interest rate is not fixed in advance. The returns depend on the performance of the assets you select and how they fare in the market.
Documents Needed for NPS Amount Withdrawal
The following documents are required for withdrawing funds from NPS:
1. Withdrawal application form
2. Original PRAN (Permanent Retirement Account Number) card
3. Verified proof of identity
4. Submission of a voided cheque.
Documents Required for Opening an NPS Account
As per the NSDL website, the necessary documents for opening an NPS account are as follows:
For Aadhaar Paperless Offline e-KYC ZIP file:
- Scanned copy of PAN and canceled cheque in jpeg, jpg, png, or pdf formats, with a file size ranging from 4 KB to 2 MB.
- Scanned signature and photograph in jpeg, jpg, or png formats, with a file size ranging from 4 KB to 5 MB.
If KYC is not completed already, the documents needed for opening an NPS account online include
Address Proof, which may include any of the following:
1. Copies of your depository account
2. Driving license
3. Electricity bill
4. ID proof from local MP, MLA, gazetted officer, municipal councillor
5. Identity card issued by your employer
6. PAN card
7. Rent receipt and credit card statement
8. School-leaving certificate
9. Water bill
Date of Birth Proof
ID Proof, which may include any of the following:
1. Driving license
2. ID proof from local MP, MLA, gazetted officer, municipal councillor
3. Identity card issued by your employer
4. PAN card
5. School-leaving certificate
Passport Sized Photograph.
NPS Application Process
Interested employees can open the NPS Account through both online and offline processes. It depends on your preference. We have provided the step-by-step process for both of them below.
NPS Apply Online
To open an NPS account online, follow these steps:
1. Visit the official eNPS website for online registration.
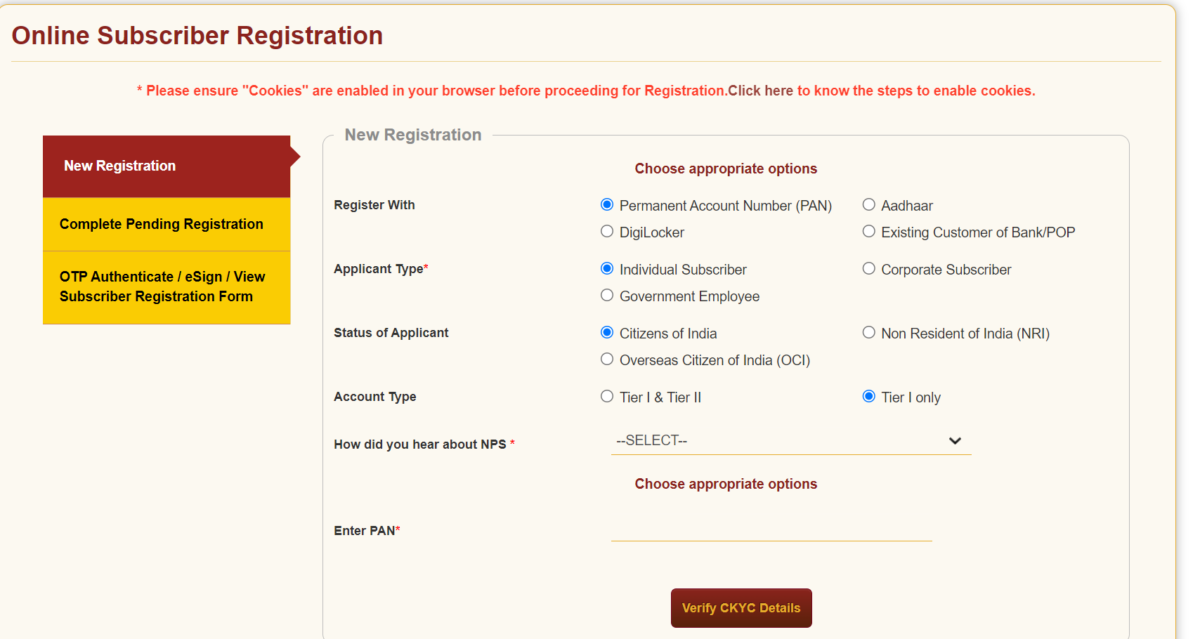
2. Click on ‘National Pension System’ and select ‘Registration.’
3. Ensure that your mobile number, Aadhaar number, and Permanent Account Number (PAN) are linked to your NPS account.
4. Validate the registration by entering the OTP sent to your registered mobile number.
5. Upon completing the registration process, you will receive a Permanent Retirement Account Number (PRAN). You can use this PRAN to log in to your profile in the future.
NPS Apply Offline
To open an NPS account offline, follow these steps:
1. Visit your nearest Point of Presence (PoP) center, a bank, or a post office.
2. Submit your Know Your Customer (KYC) documents along with a completed and signed application form.
3. After making your initial investment, the PoP center will send you a Permanent Retirement Account Number (PRAN).
4. Your welcome kit will include the PRAN and a password, which are necessary for account operations.
5. You will also need to pay a one-time registration fee of Rs. 125.
NPS Account Banks List
| NPS Bank and Non Bank List 2023 | ||
| Abhipra Capital Limited | Finwizard Technology Private Limited | Punjab National Bank |
| Alankit Assignments Limited | Gujarat Infotech Limited | Religare Broking Limited |
| Angel Broking Limited | HDFC Bank Limited | SMC Global Securities Limited |
| Arihant Capital Markets Limited | ICICI Bank Limited | State Bank of India |
| Bank of Baroda | IDBI Bank Limited | Steel City Securities Limited |
| Bank of India | Indian Bank | Stock Holding Corporation Of India Limited |
| Bank of Maharashtra | Indian Overseas Bank | Tamilnad Mercantile Bank Ltd |
| Canara Bank | Integrated Enterprises (India) Private Limited | The Karur Vysya Bank |
| Central Bank of India | Kotak Mahindra Bank Limited | The South Indian Bank Limited |
| Dayco Securities Private Limited | Marwadi Shares and Finance Limited | UCO Bank |
| DBFS Securities Limited | Muthoot Finance Limited | Way2Wealth Brokers Private Limited |
| Monarch Networth Capital Limited | Union Bank Of India | Elite Wealth Advisors Limited |
| ESAF Small Finance Bank Limited | Narnolia Securities Limited | Yes Bank Limited |
| Eureka Stock And Share Broking Services Limited | Prudent Corporate Advisory Services Limited | Punjab National Bank |